Abstract
Background: The prognosis of DLBCL patients in EZB/C3 (based on BCL2 translocation and EZH2 mutation) subgroup were varied in studies. This study aimed to describe the landscape of BCL2 translocation and other genetic alterations, correlation with outcomes in patients with novel DLBCL.
Methods: Probe capture-based high-resolution sequencing and immunohistochemistry of MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 protein expressions was performed on 373 patients diagnosed with novel DLBCL (without CNS or testicle involvement) at National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College between Jan 17th 2006 and Apr 20th 2022.
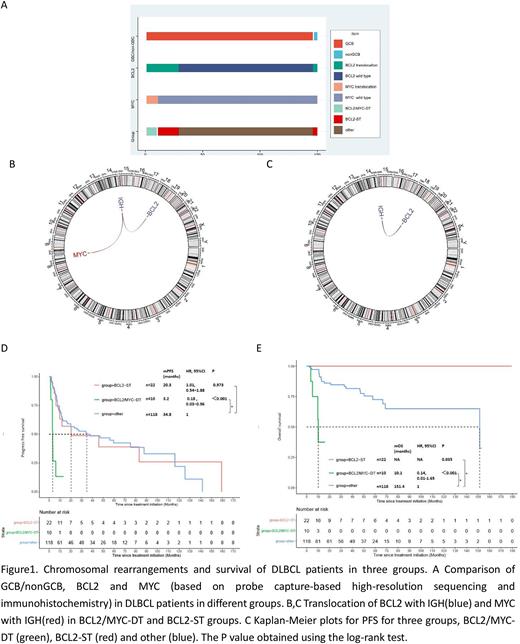
Result:150 patients diagnosed with germinal center B-cell-like (GCB, n=146) and non-GCB with BCL2 translocation (n=4) DLBCL were enrolled in this study with median follow up of 15.5 months. All patients received at least 1 dose of standard treatment. Among the cohort, 10 patients harboring BCL2 and MYC translational (BCL2/MYC-DT), BCL2 single translocation without MYC rearrangement (BCL2-ST) were seen in 22 patients (Figure 1A). IGH was the predominant rearrangement partner (100%) of BCL2 and MYC (Figure 1B,C). We identified that comparing with other patients (without BCL2 rearrangement, with or without MYC translocation, n=118), MYC/BCL2-DT group has significantly poor outcome after standard therapy(PFS: p<0.001, HR:0.18 , 95%CI:0.03−0.96; OS: p<0.001, HR:0.14, 95%CI: 0.01-1.65; Figure 1D,E). Mutations frequency of KMT2D, CREBBP, EP300, TNFRSF14, STAT6(p<0.001), FOXO1(p=0.04) and CCND3(p=0.02) were significantly different across three groups. Comparing with other patients, KMT2D, CREBBP, EP300 and EZH2 demonstrate a higher proportion across patients contained BCL2 translocation (BCL2/MYC-DT and BCL2-ST group), which was associated with epigenetic modify. The presence of CCND3 mutations tended to have negative prognostic effects on PFS (HR: 31.8, 95%CI: 2.7-371.5, P = 0.004) and OS (HR:18.6, 95%CI:2.6-133.9, P = 0.006), in patients with BCL2 translocations.
Conclusion:In DLBCL patients harboring both BCL2 and MYC translocation are most likely resulting in aggressive clinical behavior, while BCL2 translocation alone has similar prognosis with DLBCL patients without BCL2 rearrangement. DLBCL patients contained BCL2 translocation (with or without MYC rearrangement) demonstrate a higher proportion of mutation associated with epigenetic modify, which may benefited from epigenetic therapy.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal